Motion of Center of Mass
Motion of Center of Mass: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Velocity of Centre of Mass, Acceleration of Centre of Mass, and Explosion of a Projectile in Its Path.
Important Questions on Motion of Center of Mass
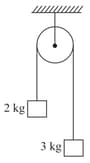
Two blocks of masses and are attached with massless string passing over a fixed frictionless pulley as shown in the figure. When released, the velocity of the centre of mass of the system of two blocks after 1.5 seconds is (Acceleration due to gravity )
In case of an isolated system, the centre of mass of the system moves with a constant _____.
A uniform rod of length is fixed at one end. It is initially held vertically upward, then released. Find the vertical reaction at hinge when it becomes horizontal.
Two masses and are connected by a light inextensible string and suspended by means of a weightless pulley as shown in the figure. Assuming that both the masses start from rest, the distance travelled by center of mass in two seconds is (Take )
Two particles of equal mass have velocities and . First particle has an acceleration while the acceleration of the other particle is zero. The centre of mass of the two particles moves in a path of
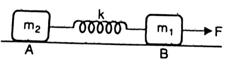
Two blocks of masses and are connected by a spring of negligible mass and placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. An impulse gives a velocity of to the heavier block in the direction of the lighter block. The velocity of the centre of mass in is , then
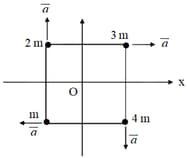
At an instant, four particles are having masses and acceleration as shown in the figure. Find the acceleration of center of mass of the system.
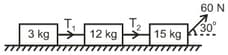
Three masses are connected as shown in figure on a horizontal frictionless surface and pulled by a force of 60 N. The tensions T1 and T2 are in the ratio
A solid sphere of mass M and radius 2R rolls down an inclined plane of height without slipping. The speed of its centre of mass when it reaches the bottom is
Two blocks masses and are connected by a spring of spring constant The block of mass is given a sharp impulse so that it acquires a velocity towards right. Find the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer.
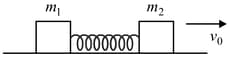
The masses and are placed as shown in figure and released if all the surfaces are frictionless, the relation between the horizontal accelerations of and
A bomb of mass 1 kg is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of . After 5 seconds it explodes into two fragments. One fragment of mass 400 gm is found to go down with a speed of . What will happen to the second fragment just after the explosion?
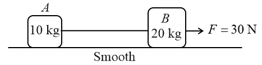
Two blocks A and B are connected by a massless string (shown in fig.) A force of 30 N is applied on block B. Find the distance travelled by centre of mass in 2 seconds starting from rest
Two bodies A and B of masses and respectively are connected by a massless spring of force constant k. A constant force F starts acting on the body A at . Then
A solid cylinder of mass m and radius R rolls down an inclined plane of height h without slipping. The speed of its centre of mass when it reaches the bottom is
A thin rod of length L is vertically straight on horizontal floor. This rod falls freely to one side without slipping of its bottom. The linear velocity of centre of rod when its top end touches floor is
Two particles and of mass and respectively are projected in the directions shown in figure with speeds and , initially they were apart. Find the maximum height attained by the center of mass of the particles.
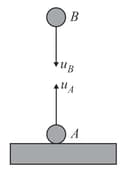
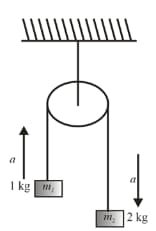
Two blocks of equal mass are tied with a light string, which passes over a massless pulley as shown in figure. The magnitude of acceleration of centre of mass of both the blocks is ( neglect friction everywhere )
A man of mass stands at one end of a plank of length which lies at rest on a frictionless surface. The man walks to the other end of the plank. If the mass of the plank is , the distance that the man moves relative to the ground is -
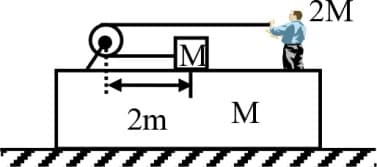
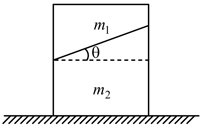
A block of mass is tied to one end of a massless rope. The other end of the rope is in the hands of a man of mass as shown in the figure. The block and the man are resting on a rough wedge of mass as shown in the figure. The whole system is resting on a smooth horizontal surface. The man pulls the rope. Pulley is massless and frictionless. What is the displacement of the wedge when the block meets the pulley ?
(Man does not leave his position during the pull)